Featured
Example Of Covalent Network Solid
Example Of Covalent Network Solid. Many minerals have networks of covalent bonds. Correct option is c) network solid is a type of solid in which the constituent atoms are held together strongly by a regular parttern of covalent bonds or its network on atoms.
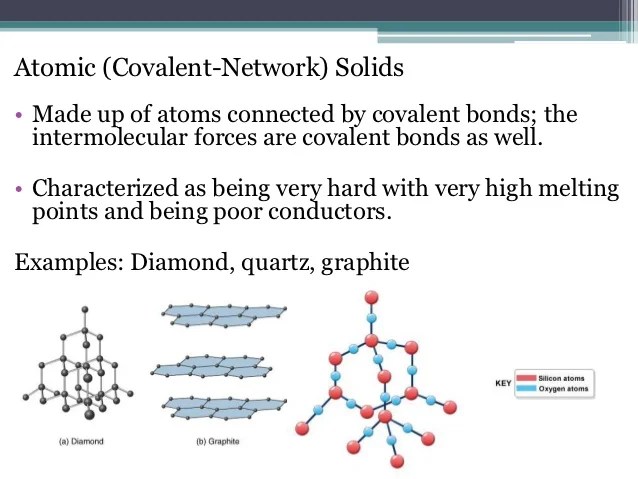
A common example of network solids is diamond (pure. The key difference between molecular solid and covalent network solid is that molecular solid forms due to the action of van der waal forces whereas covalent network solid forms due to the action of covalent chemical bonds. Example of a solid covalent compound.
For Example, The Melting Point Of Diamond Is Above 3500 °C Which Is The Highest Among All.
The key difference between molecular solid and covalent network solid is that molecular solid forms due to the action of van der waal forces whereas covalent network solid forms due to the action of covalent chemical bonds. Atoms in covalent solids are covalently bonded with their neighbors, creating, in effect, one giant molecule.; Covalent network solids include crystals of diamond, silicon, some other nonmetals, and some covalent compounds such as silicon dioxide (sand) and silicon carbide (carborundum, the abrasive on sandpaper).
A Substance Has A Melting Point Of 8040C, Is Insoluble In Water And Is A Good Insulator Of Electricity.
The classic example is diamond; Therefore, silicon carbide ( sic) is an example of a covalent solid. Similarly, a covalent solid cannot melt in the.
100% (5 Ratings) Sio2 Is A Covalent Network Solid.
Because of the way atoms are arranged, a network solid may be considered a type of macromolecule. Which one of the following is an example of a covalent network solid? In network solid types, traditional chemical bonds together hold chemical subunits.
While, Limestone (Caco 3) And Table Salt (Nacl) Are Ionic Solids.
Dry ice (solid (co 2)) and i 2(g) are molecular solids. Boron, carbon and silicon all form covalent networks. Example of a solid covalent compound.
This Sharing Results In A Stable Balance Of Attractive And Repulsive Forces Between Those Atoms.
In addition, these types of crystalline solids are usually hard, fragile and tend to show a very high fusion point. Examples of covalent solids include diamond and silica (sio 2 ). The bonding or relationship between the chemical subunits, nevertheless, is similar within the subunits, which results in an unending network of chemical bonds.
Popular Posts
An Example Of A Two Point Violation Includes Reckless Driving
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Comments
Post a Comment